IPC Standards
IPC Standards

IPC Standards: Standards that encompass the value chain
Did you know that IPC standards are developed for every step of the production and assembly process?
From design and purchasing to assembly and approval, IPC provides standards that ensure high quality, reliability, and consistency in the assembly of electronic products. Like any manufacturing process that employs a step-by-step approach, IPC standards are interdependently constructed.Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)
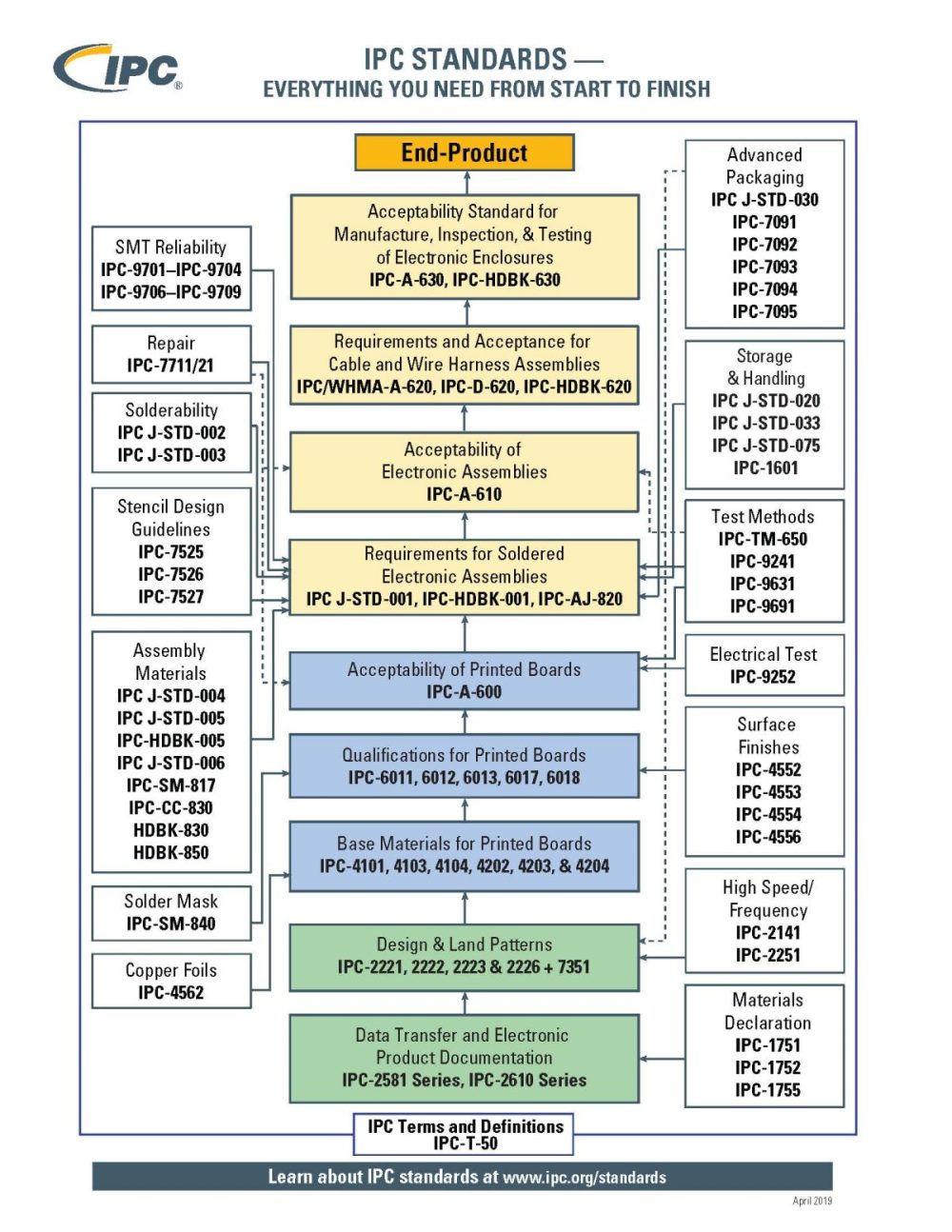
IPC Standards Basic Structure
The IPC standards start with PCB design and base materials, and have at their core PCB performance and quality standards (600, 6012), soldering process standards (001), and quality standards for electronic assemblies and wire harnesses (610, 620). The detailed and specialized content related to each process is then coordinated and standardized for specific areas. This includes components and materials, solder masks, solderability evaluation, BGA and BTC (bottom surface electrode components), conformal coating, etc. In addition, IPC-7711/21 has been adopted worldwide as a rework/repair procedure after assembly, and TM-650, which lists quality test methods. In addition to standardization on the product axis, additional industry-specific requirements, such as aerospace, automotive and in-vehicle, have been widely adopted around the world.
Three Reasons Why So Many Companies Adopt IPC Standards
The fact that IPC is recognized and used as the de facto standard in the global electronics industry is a very important factor behind its adoption by many companies around the world. In Japan, various standards and standardizations exist, including domestic standards, but in the global market, IPC is increasing its presence as the one and only quality standard in the electronics market. The fact that users who actually use and require the standard can participate in active discussions and bring scientific supporting data to be agreed upon and involved in decisions is also an important reason for the adoption of IPC.
Reason #1
Most important quality and reliability.
Applying the IPC standard to all manufacturing processes will improve performance, extend service life, and achieve compliance with lead-free regulations.

Reason #2
The IPC standard, adopted by many suppliers, is the “common language” of the electronics industry.
Recognition of quality with overseas employees is also standardized.

Reason #3
Contributing to Cost Containment
Standards-based design and material procurement create an assembly process that passes rigorous quality tests, minimizing delays, remanufacturing, and waste that can lead to cost overruns.
IPC standards developed for various production sites
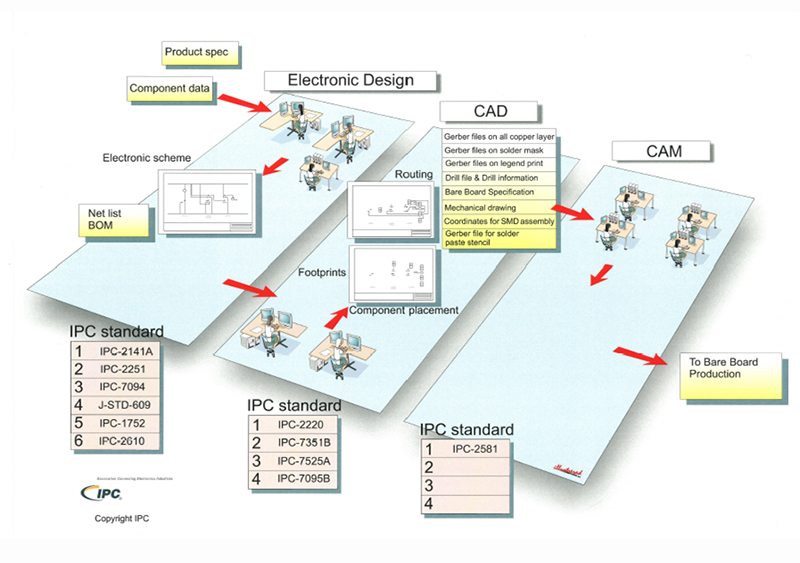
Design
The IPC standardizes not only PCB pattern design, PCB materials, and plating processes, but also stencil design, solder masks, and other PCB manufacturing design-related issues. IPC-2221, in particular, is often adopted as a setting value in PCB design CAD.
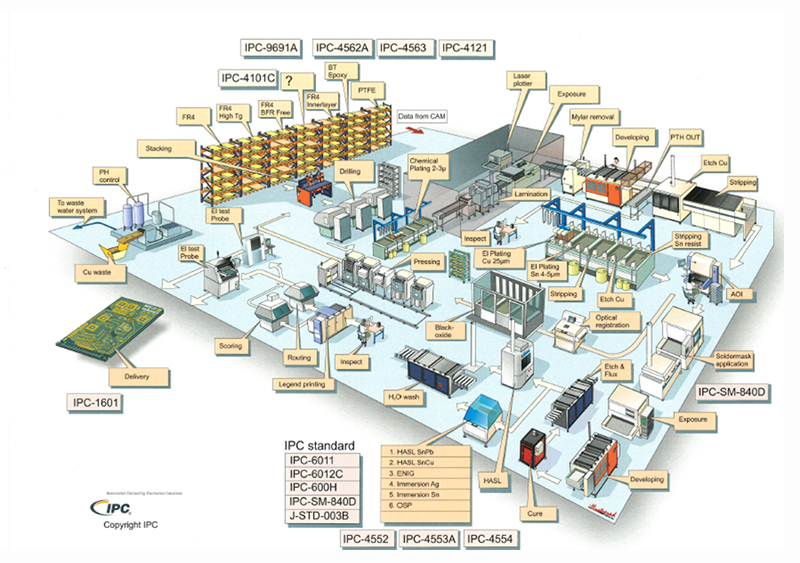
Base
Base includes PCB materials (substrate) and components as well as solder materials. Solderability of component leads and PCB electrode side, paste and solder alloys, etc. It also includes base materials used on mounting, such as conformal coatings.
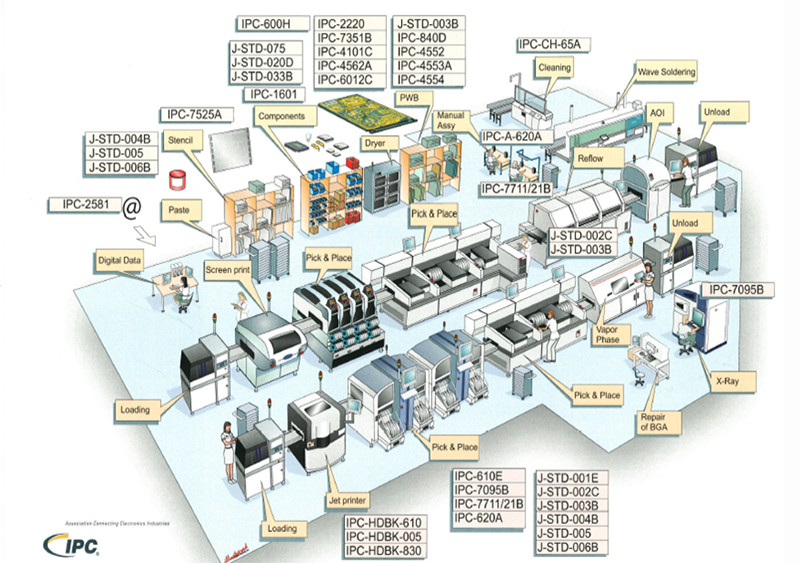
Assembly
Assembly is one of the most important processes in which IPC is employed. It includes soldering process and PCBA assembly process as well as quality standards for PCBA assemblies (visual evaluation). Also, wire harnessing and post-mounting rework/repair procedures are widely adopted.
Three quality classes classified by product category
Class 1
General electronics products
Products that are appropriate for applications where the main requirement is the function of the completed electronic assembly.

Class 2
Application-specific electronic products
Includes products for which continuous performance and long life and uninterrupted service are required but are not critical factors. The end-use environment is generally not a cause of failure.

Class 3
High Performance Electronics
Sustained high performance or ability to function on demand is important, no equipment interruptions are allowed, and the end-use environment is very demanding and must function as needed, such as in life support and other critical systems.

Reference Videos

Use IPC for Quality Evaluation in British National Laboratory
UK Laboratory Performs Sample Evaluation by Japan Unix Soldering Robots

 日本語
日本語 中文
中文 Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español